Your Guide to Buying Diamonds
The four C's explained
When referring to diamonds you may of heard about the "4 C's". This term stands for Carat, Clarity, Colour and Cut. Here's some information to help you understand a little bit about these precious gems.

Carat
Diamonds vary in price according to cut, clarity, colour and carat. These characteristics are known as the 4 C’s. Carat refers to the weight of a diamond. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. One carat can also be divided into 100 “points.” Larger diamonds are found less frequently in nature, which places them at the rarest level of the Diamond Quality Pyramid, a 1-carat diamond will cost more than twice a 1/2-carat diamond (assuming colour, clarity and cut remain constant)

Clarity

Colour
Colour refers to the degree to which a diamond is colourless. Diamonds are found in almost every color of the rainbow, but white-coloured diamonds remain most popular. Colour differences are very subtle and it is very difficult to see the difference between, say, an E and an F. Therefore, colours are graded under controlled lighting conditions and are compared to a master set for accuracy. Truly colourless stones, graded D, treasured for their rarity, are highest on the Diamond Quality Pyramid. Colour, however, ultimately comes down to personal taste. Nature has also created diamonds in intense shades of blue, green, yellow, orange, pink or – rarest of all – red. These diamonds are called ‘coloured fancies’ and are extremely rare and highly treasured.

|
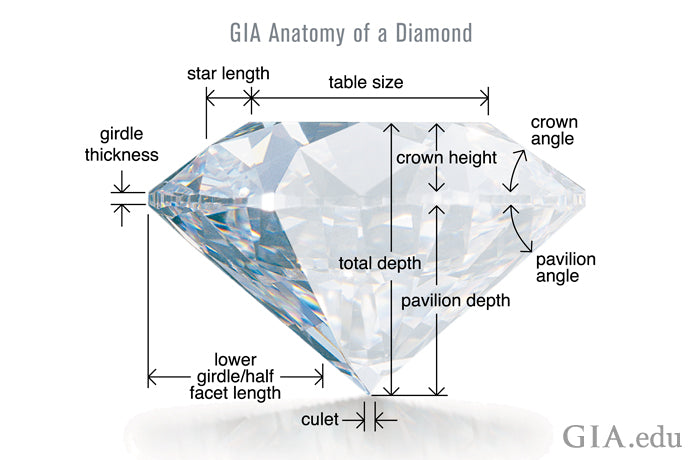
Cut
Cut refers to the angles and proportions of a diamond. Nature determines so much about a diamond, but it takes a master cutter to reveal the stone’s true brilliance, fire and ultimate beauty. Based on scientific formulas, a well-cut diamond will internally reflect light from one mirror-like facet to another and disperse and reflect it through the top of the stone. This results in a display of brilliance and fire, thereby placing well-cut diamonds higher on the Diamond Quality Pyramid than deep or shallow-cut diamonds. Diamonds that are cut too deep or too shallow lose or leak light through the side or bottom, resulting in less brilliance and ultimately, value.